

If ‘f’ is a continuous function defined on the closed interval and F is an anti-derivative of ‘f’. If ‘f’ is a continuous function on the closed interval and A (x) is the area function. This helps us define the two basic fundamental theorems of calculus. This is denoted by A(x) and represented as follows: The area of this shaded region depends on the value of ‘x’. However, the assertions made below are true for other functions as well. Note: We are assuming that f(x)> 0 for x ∈. If ‘x’ is a point in, then ∫ a x f(x) dx represents the area of the shaded region in the figure above. This includes integration by substitution, integration by parts, trigonometric substitution and integration by partial fractions.By definition, ∫ a b f(x) dx is the area of the region bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis and the coordinates ‘x = a’ and ‘x = b’. These use completely different integration techniques that mimic the way humans would approach an integral. As a result, Wolfram|Alpha also has algorithms to perform integrations step by step. While these powerful algorithms give Wolfram|Alpha the ability to compute integrals very quickly and handle a wide array of special functions, understanding how a human would integrate is important too. Another approach that Mathematica uses in working out integrals is to convert them to generalized hypergeometric functions, then use collections of relations about these highly general mathematical functions. Even for quite simple integrands, the equations generated in this way can be highly complex and require Mathematica's strong algebraic computation capabilities to solve. One involves working out the general form for an integral, then differentiating this form and solving equations to match undetermined symbolic parameters. There are a couple of approaches that it most commonly takes. Instead, it uses powerful, general algorithms that often involve very sophisticated math. Integrate does not do integrals the way people do. It calls Mathematica's Integrate function, which represents a huge amount of mathematical and computational research. Wolfram|Alpha computes integrals differently than people. Wolfram|Alpha can solve a broad range of integrals How Wolfram|Alpha calculates integrals
A common way to do so is to place thin rectangles under the curve and add the signed areas together.

Sometimes an approximation to a definite integral is desired.
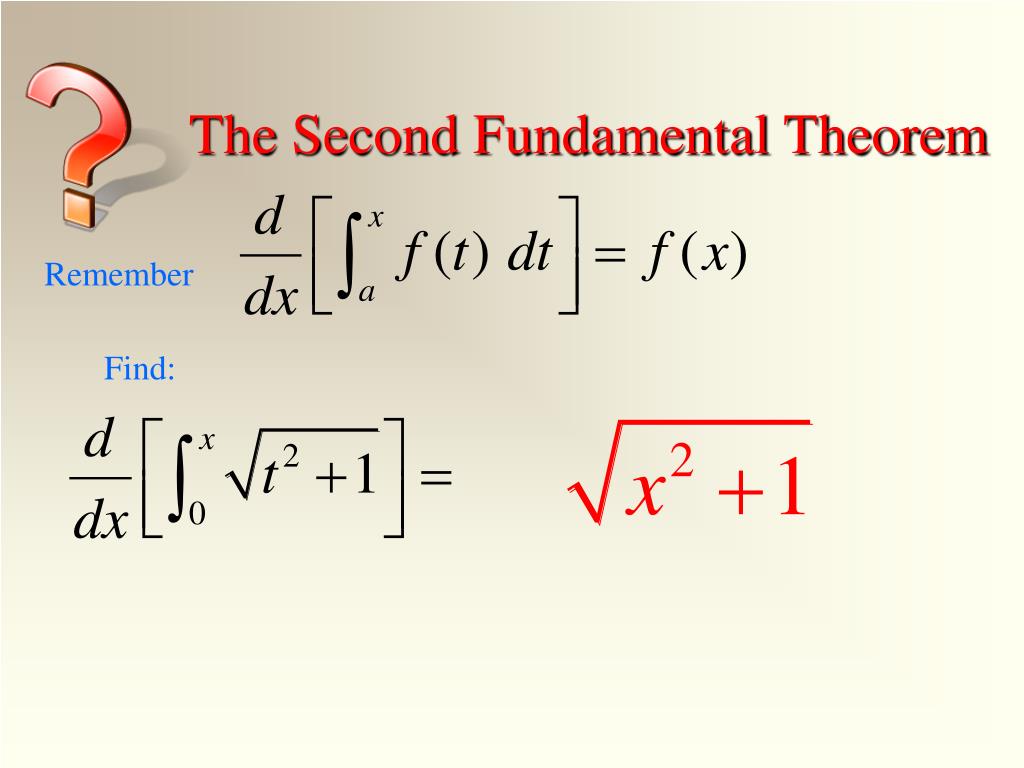
This states that if is continuous on and is its continuous indefinite integral, then. īoth types of integrals are tied together by the fundamental theorem of calculus. The definite integral of from to, denoted, is defined to be the signed area between and the axis, from to. Since the derivative of a constant is 0, indefinite integrals are defined only up to an arbitrary constant. The indefinite integral of, denoted, is defined to be the antiderivative of. What are integrals? Integration is an important tool in calculus that can give an antiderivative or represent area under a curve. Partial Fraction Decomposition Calculator.
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS FORMULA GENERATOR
Get immediate feedback and guidance with step-by-step solutions for integrals and Wolfram Problem Generator integrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi.
FUNDAMENTAL THEOREM OF CALCULUS FORMULA HOW TO
Here are some examples illustrating how to ask for an integral using plain English. To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary. Use Math Input above or enter your integral calculator queries using plain English. The Wolfram|Alpha Integral Calculator also shows plots, alternate forms and other relevant information to enhance your mathematical intuition. Wolfram|Alpha is a great tool for calculating antiderivatives and definite integrals, double and triple integrals, and improper integrals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
